| Step by Step illustration of work procedure |
|
1. Preparing plan of Hippodrome fresco area according to the archaeological topographic grid.
1.1. From an established Zero point, Hippodrome fresco
was measured meter by meter and marked on the site and also on the plan. (Archaeological topographic grid - usually 5 by 5 meters grid measured and marked on the site before archeological digging. Archaeological square is every square of this grid where digging was performed.)
|
 |
|
2. Take color photography with digital camera.
The surface of the fresco in every archaeological square was covered with couple of pictures taken by hand from close distance with overlapping about 20%.
|
 |
| 3. Importing the images into
the computer.
Every image were imported and saved with file name compound archaeological square number and sequence letter.
|
 |
| The images were rectified
and assembled using PhotoShop program. At the beginning were created
complete images showing the fresco surface of every archaeological square.
After that every three of them were scaled and placed according to the
specific section of Hippodrome fresco Plan.
|
 |
| 5. Tracing the outlines of
the plaster and fresco design.
|
 | 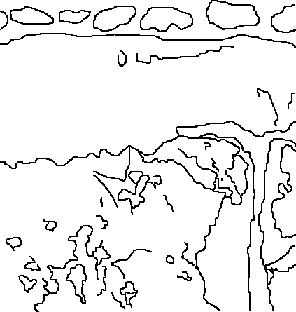 |
| 6. Vectorization of the
Raster files.
This is another digital transformation decreasing one more time the file size. The advantage of this file format is also a possibility to change color and type of the line.
|
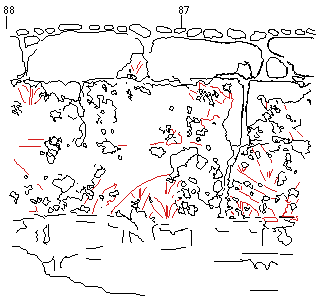 |
| The files of outlines were
imported to Free Hand application. After vectorization the outlines were
divided in two colors: fresco design line - red and the plaster -
black.
This is already the Base-map.
|
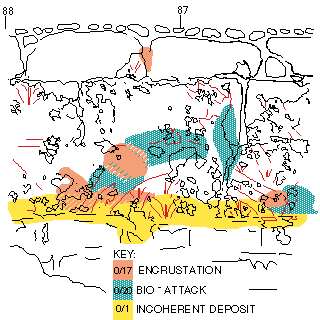 |
| 7. Use the Base-map for
condition recording.
For this work was used also Free Hand. This application allows marking areas with different colors on different layers. The conservation information was mapped on according to Caesarea Color Code List of Status of Conservation and Modern Intervention. |